Italian Alder
Alnus cordata
The Italian alder produces cone-like structures as its fruiting bodies.
About
Italian Alder
The Appearance
A medium to large deciduous tree with a conical shape and glossy, dark green leaves that remain on the tree until late autumn.
The Produce
These structures are referred to as strobiles or catkins.
The Flowers
Produces long, yellow catkins in early spring, followed by small, woody cones.
The Leaves
These leaves are elliptical in shape, featuring a glossy, dark green colour on the upper surface.
The Habitat
Prefers moist, well-drained soils and full sun. Commonly found along riverbanks and in wetlands.
The Ecology
Provides habitat and food for various wildlife, including birds and insects. The roots improve soil fertility by fixing nitrogen.
The Culture
Used in traditional medicine and for timber, particularly in waterlogged conditions as the wood resists decay.
Fun Facts
The Italian Alder is valued for its ability to improve soil fertility through its symbiotic relationship with nitrogen-fixing bacteria in its roots.
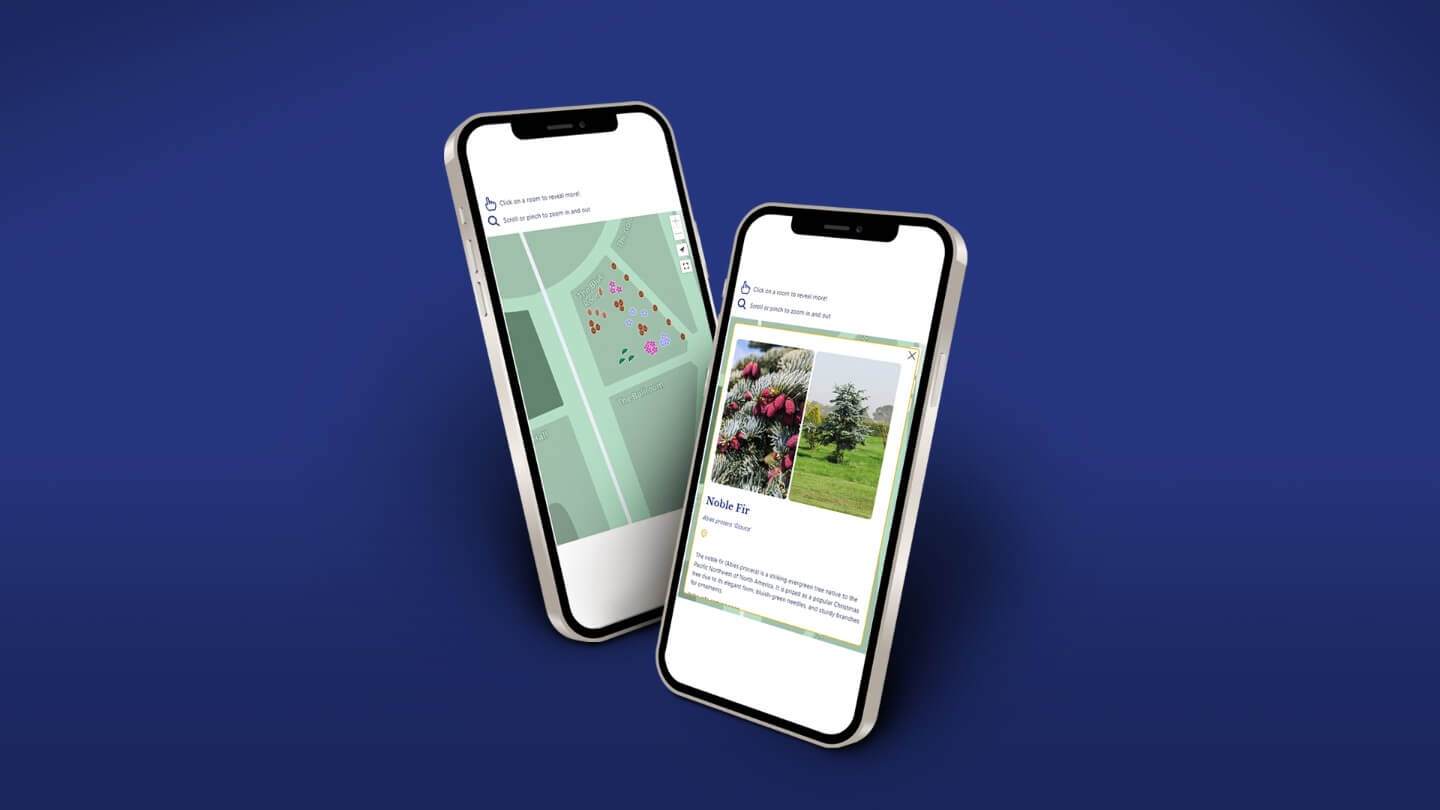
Explore Deeper With The Interactive Map
Unleash your inner explorer with our interactive map of the Arboretum. This live map labels the location of every tree in the arboretum, providing detailed information on each one.
Dive into the fascinating stories behind each tree, learn about their origins, characteristics, and unique attributes. The interactive map is your perfect companion for an engaging and educational adventure. Discover the rich tapestry of nature with just a few clicks!
Arboretum Index
Stay at East Yorkshire’s most peaceful holiday park
